Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

All businesses must face different kinds of costs throughout their operation, which can be grouped into fixed cost or variable cost. Understanding fixed cost is of great importance for companies to price their goods or services reasonably.
In this article, you will learn about fixed costs, how total fixed costs and average fixed cost can be measured, examples of fixed cost, as well as pros and cons of fixed cost.
Without further ado, here is the definition.
Fixed cost is the expense that does not change in tandem with changes in demand or revenue over a certain period of time. Fixed cost is independent of the number of business activities because it is more of a periodic cost. Fixed costs are also referred to as indirect costs or overhead.
The business cannot change their fixed costs even if they decide to decrease operating expenses. Instead, fixed cost is usually set by an external body like a property owner or bank. Rent fees, insurance, and staff’ salary are some examples of fixed costs.
Total fixed cost, or the overall expense of every kind of fixed costs, is usually calculated over a short period of time, for example, a month or half a year. Although the amount of money linked with fixed costs may not vary based on sales, they will increase or decrease depending on other variables. Your landlord, for instance, can raise the lease on your office. Your operating expenses will increase, but this increase is not related to production or revenue. Thus, as these costs vary, it is advised to measure only the fixed costs in the short term.
Fixed cost is one of the two main contributors to the overall production cost. On the other hand, variable cost is business expenses that can vary depending on demand or revenues. Goods’ materials and facilities are examples of variable costs.

Think of the variable cost and fixed cost this way. As an adult, you may need to pay a monthly rent or contract, electric bill, vehicle payment, housing, travel costs, and groceries. Expenses like groceries, petrol expenditures, and childcare will increase if you have children, and these expenses are your variable costs
Although your variable costs escalate after having a family, for as long as you are in the same home and ride the same vehicle, your monthly mortgage, utility bill, travel expenses, and car payment do not change. These expenses are your fixed costs, and no matter what adjustments you make to your schedule, you pay the same price.
Likewise, let’s say a startup e-commerce business pays for warehouse space to manage its inventory and 10 customer service employees to handle order inquiries. But all of a sudden, it signs a contract that requires another five paid customer service reps. The labor’s variable costs of this startup rise, while warehouse’s fixed cost remains the same.
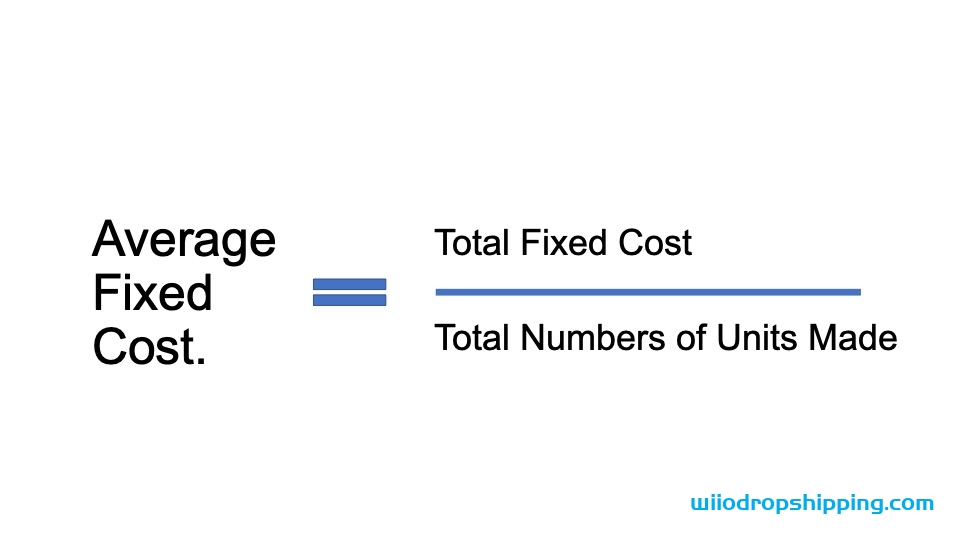
Average fixed cost, also referred to as fixed cost per product, assigns each piece of merchandise a cost to compensate for all the fixed costs needed to operate the company.
Average fixed cost gives you an idea of how much the company is supposed to be paying every time a unit of a commodity is produced — before considering the variable costs in order to actually manufacture it. Average fixed cost allows companies to decide a price point on their goods. Knowing the average fixed cost is vital because if it is not reflected in the price of the company’s commodity, that company will not make any profits.
If you have come this far, you have probably got the gist of a handful of fixed cost examples we are already paying as individuals, things like your monthly mortgage, utility bill, travel expenses, and car payment, etc.
However, fixed cost for your company is another story. Your company could incur a variety of fixed costs that you barely pay in your personal life. In fact, some variable costs for people are fixed costs for companies.
Calculation of your fixed costs is definitely not the most enjoyable part of growing your business. But understanding what they are and when you need to pay for each of them gives you the financial security you need to serve and satisfy your customers.

For every emerging business to bear in mind, here’s a master list of fixed costs:

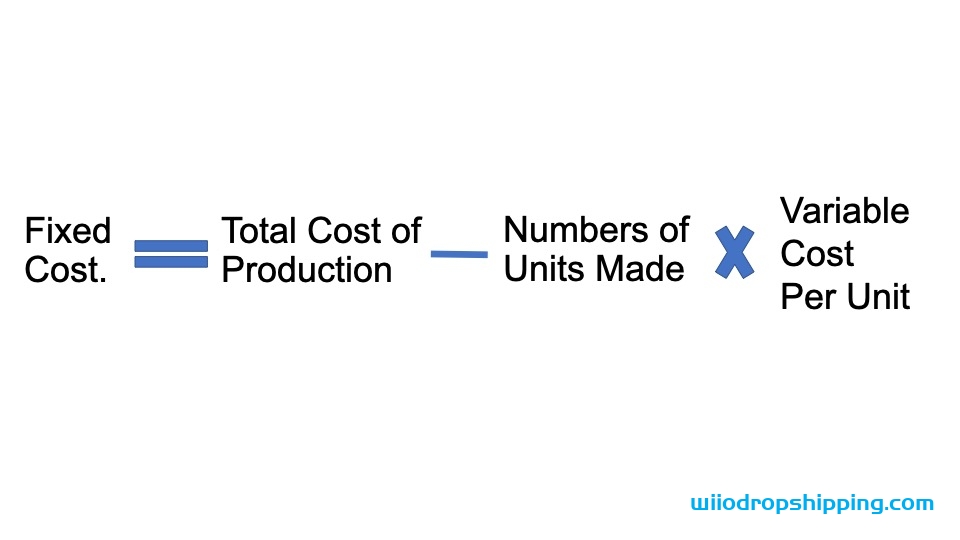
We can derive the Fixed Cost formula by first multiplying the number of units produced and the variable production cost per unit, then subtracting the result from the overall production cost. It is interpreted mathematically as below
** Fixed Cost = Total Cost of Production – Number of Units Produced * Variable Cost Per Unit **
Average fixed cost gives you an idea of how much the company is supposed to be paying every time a unit of a commodity is produced — before considering the variable costs in order to actually manufacture it.
Average fixed cost allows companies to decide a price point on their goods. Knowing the average fixed cost is vital because if it is not reflected in the price of the commodity of the company, that company will not make any profits.
You can calculate the formula for fixed costs by using the following steps:
Step 1: First, calculate the variable production cost per unit, which may be the sum of different production costs, such as labor costs, raw material costs, commissions, etc. These costs are variable in nature and change as the production rate or market volume rises or decreases.
Step 2: Then, calculate the number of units made during a fixed production period.
Step 3: Multiply the variable cost per unit (step 1) and the number of unit production (step 2) to get the total variable cost of production.
Total Variable Cost of Production = Variable Cost Per Unit * No. of Units Produced
Step 4: Determine the total cost of production of the company during a time period (aka. the total of all costs combined during production cost)
Step 5: Finally, calculate the total fixed production cost by subtracting the total variable cost in step 3 from the total production cost in step 4. You can see the formula below.
Fixed Cost = Total Production Cost – Variable Cost
or
Fixed Cost = Total Production Cost – Number of Units Produced * Variable Cost Per Unit
Let us look at the XYZ Toy Company. The number of toys produced in May 2020 is 20,000, according to the production manager. The total cost of production for that month was $100,000 according to its accounts department. Calculate the fixed production cost given the average variable cost per unit for XYZ Toy Company is $3.
Solution:
We have
| Total cost of production = $100,000 (A) |
|---|
| Variable cost per unit = $3.00 (B) |
| Number of units produced = 20,000 (C) |
We can calculate the fixed cost of production of XYZ Toy Company for May 2020 as follows.
Fixed cost of production of XYZ Toy Company = A – B*C = 100,000 – 3.00 * 20,000 = $40,000.
Let’s look at another example of company XYZ Shoe Company. The production data for March 2020 is as below:
Solution:
We have,
| Total cost of production = $150,000 (A) |
|---|
| Cost for raw material cost per unit = $35 (B) |
| Labor expense per hour = $45 per hour (C) |
| Time needed to produce a unit = 45 min = 45 / 60 hours = 0.75 hours (D) |
| Number of units produced = 2,000 (E) |
First, we calculate the variable cost per unit as:
Therefore, we can calculate the Fixed Cost of production for XYZ Shoe Company in March 2020 as.
Therefore, the Fixed Cost of production for XYZ Shoe Company in March 2020 is $12,500.
XYZ Dolls manufactures children’s toy dolls. To set a fair price for the goods, the firm has to calculate the fixed cost.
XYZ Dolls make a summary of any monthly cost that they have. They split the aggregate list into variable costs and fixed costs. Building rent ($4,000), employee salaries ($100,000), supplies ($3,000) and a website ($300) are their fixed costs.
To measure the cumulative fixed costs, XYZ Dolls adds up all its separate fixed costs:
$4000 + $100,000 + $3000 + $300 = $107,300
Now, XYZ Dolls realizes that they need to make up for $107,300 in their products’ price. To determine the fair price for a doll, they need to calculate the average fixed cost (aka. fixed cost per unit).
For example, assume XYZ Dolls has 8,000 dolls on stock for sales. To get the average fixed cost, they divide $107,300 (the total fixed cost) by 8,000 (the unit number for sale). The average fixed cost, or fixed cost per unit, is 107,000 / 8000 = $13.4.
XYZ Dolls must add that average fixed cost of $13.40 to the sales price to make sure they make up for the fixed cost.
What if XYZ Dolls wants to raise their profit number? Increasing production and producing more dolls is one way to do this. XYZ Dolls company is paying $13.40 on average fixed costs at the production rate of 8,000 dollars a month. The company can increase its production to 10,000 dolls a month. Now, their average fixed cost is only $10.73. In other words, the XYZ Dolls company can make an extra $2.67 in profit per doll sold without changing any other operating expenses.
The concept of fixed costs is crucial to consider since it is one of the two main components of the overall production expense, the other being the variable cost. Fundamentally, fixed costs are seen as the sort of fee that, regardless of the company’s level of economic performance, rarely varies.
Nevertheless, it should be noted that fixed costs are not unchanged, and during capacity growth or economic recession, it varies. Theoretically, fixed costs serve as a deterrent to potential competitors in capital-intensive sectors, effectively eliminating the possibility of smaller or younger players competing. Depreciation charges, staff wages, contract leasing, insurance fees, etc., are some of the primary examples of fixed costs.
We can derive the Fixed Cost formula by first multiplying the number of units produced and the variable production cost per unit, then subtracting the result from the overall production cost.
Calculation of your fixed costs is definitely not the most enjoyable part of growing your business. But understanding what they are and when you need to pay for each of them gives you the financial security you need to serve and satisfy your customers.